Summary: The macro data from the past month continues to mostly point to positive growth. On balance, the evidence suggests the imminent onset of a recession is unlikely.
The bond market agrees with the macro data. The yield curve has 'inverted' (10-year yields less than 2-year yields) ahead of every recession in the past 40 years (arrows). The lag between inversion and the start of the next recession has been long: at least a year and in several instances as long as 2-3 years. On this basis, the current expansion will likely last through 2018 at a minimum. Enlarge any image by clicking on it.
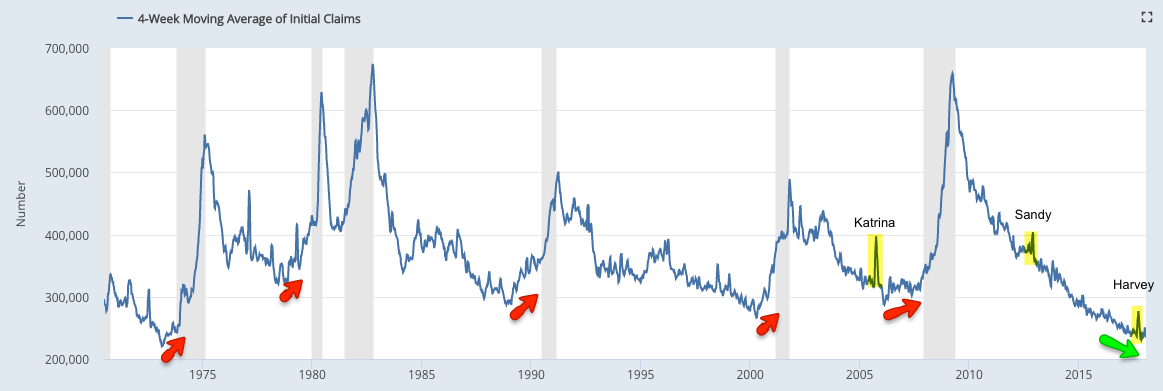
Unemployment claims are also in a declining trend; historically, claims have started to rise at least 6 months ahead of the next recession. Note that recent hurricanes had a short-term negative impact on employment data but recent claims are already near a 40+ year low and are likely to exceed the November low in the next week.
New home sales made a new 10 year high in November. In the past 50 years, more than a year has lapsed between the expansion's high print in new home sales and the start of the next recession.
Real retail sales (excluding gas) made a new all-time high (ATH) in December. The trend higher is strong, in comparison to the period prior to the past two recessions.
Here are the main macro data headlines from the past month:
Employment: Monthly employment gains have averaged 176,000 during the past year, with annual growth of 1.4% yoy. Employment has been driven by full-time jobs, which rose to a new all-time high in January.
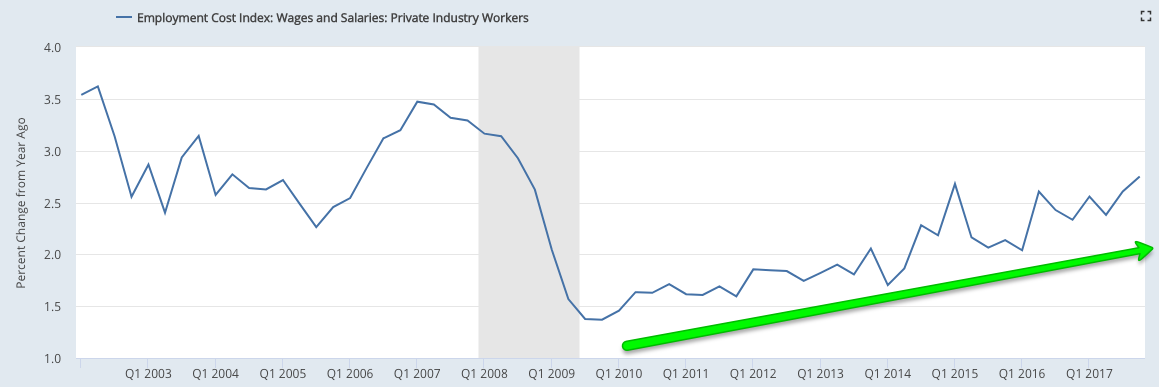
Compensation: Compensation growth is on an improving trend, recently notching the highest growth in the past 9 years. Hourly wage growth was 2.9% yoy in January, while the 4Q17 employment cost index grew 2.8% yoy.
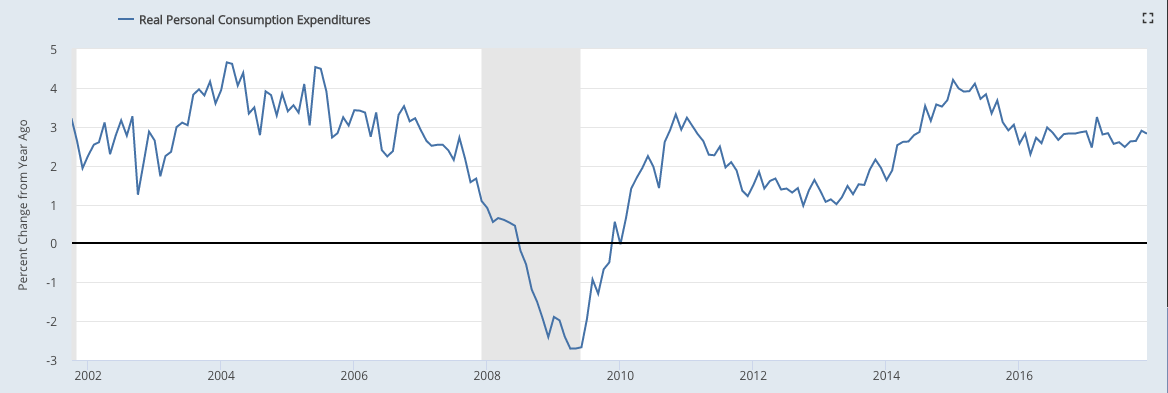
Demand: Real demand growth has been 2-3%. In December, real personal consumption growth was 2.8%. Real retail sales (including gas) grew 3.3% yoy in December, making a new ATH.
Housing: New home sales grew 14% yoy in December. Housing starts were at the second highest level of the past 10 years in November but fell 6% yoy in December. Multi-family units remain a drag on overall development.
Manufacturing: Core durable goods rose 8.8% yoy in December, the second-best annual growth rate in 4 years. The manufacturing component of industrial production grew 2.6% yoy in December, near the highest rate of growth in over 3 years.
Inflation: The core inflation rate remains near (but under) the Fed's 2% target.
Our key message over the past 5 years has been that (a) growth is positive but slow, in the range of ~2-3% (real), and; (b) current growth is lower than in prior periods of economic expansion and a return to 1980s or 1990s style growth does not appear likely.
This is germane to equity markets in that macro growth drives corporate revenue, profit expansion and valuation levels. The simple fact is that equity bear markets almost always take place within the context of an economic decline. Since the end of World War II, there have been 10 bear markets, only 2 of which have occurred outside of an economic recession (read further here).
The highly misleading saying that "the stock market is not the economy" is true on a day to day or even month to month basis, but over time these two move together. When they diverge, it is normally a function of emotion, whether measured in valuation premiums/discounts or sentiment extremes.
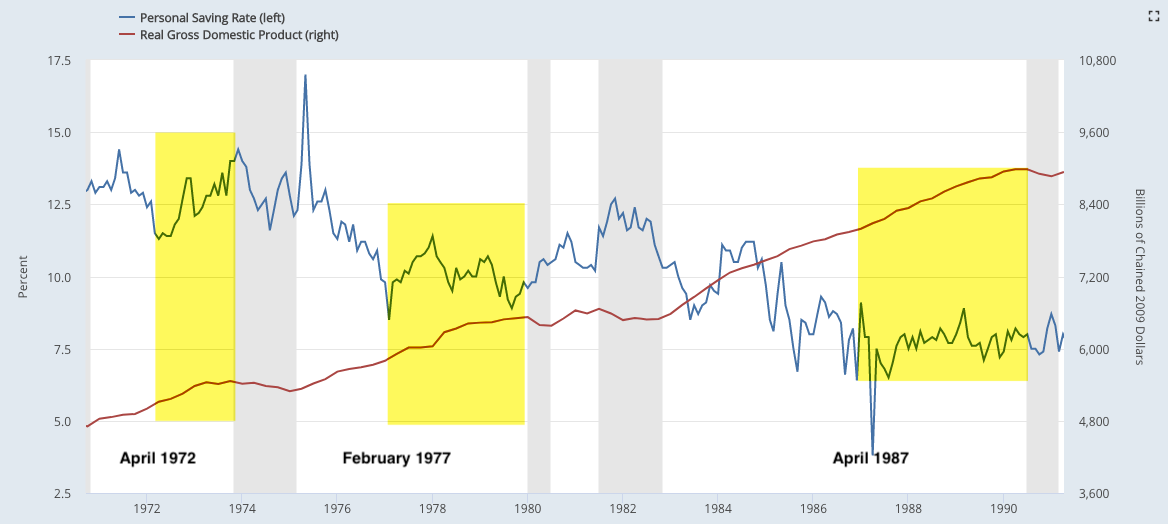
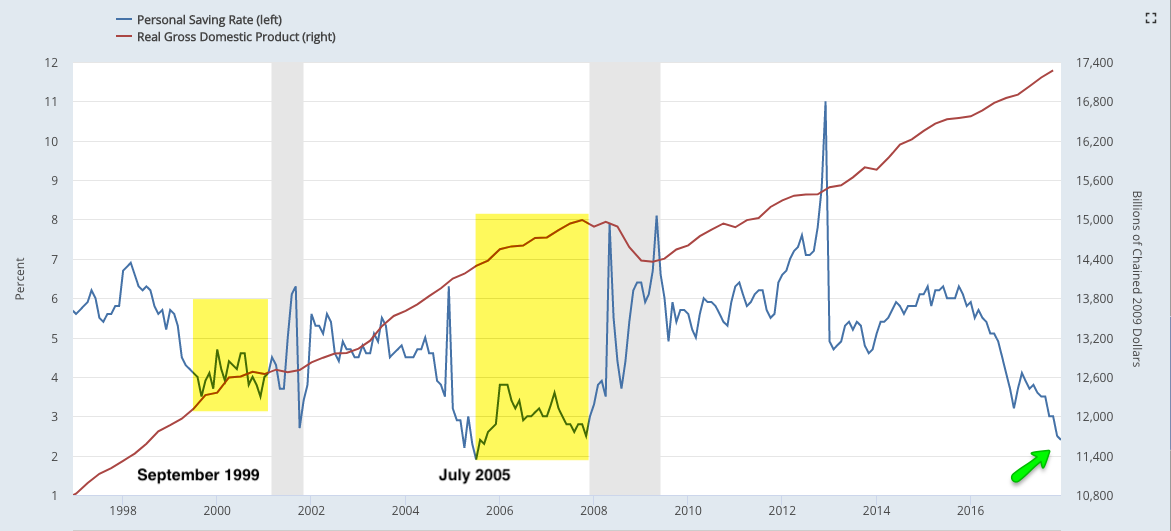
Macro data will likely underperform expectations in 1H18. Why? Macro data ended 2017 well ahead of expectations. During the current expansion, that has led to underperformance of macro data relative to expectations into the following mid-year (yellow shading). 2009 and 2016 had the opposite pattern: macro data underperformed expectations into the prior year-end and then outperformed in the first half of the year (green shading).
A valuable post on using macro data to improve trend following investment strategies can be found here.
Let's review the most recent data, focusing on four macro categories: labor market, end-demand, housing, and inflation.
Employment and Wages
The January non-farm payroll was 200,000 new employees minus 24,000 in revisions for the prior two months.
Employment growth is decelerating. In the past 12 months, the average monthly gain in employment was 176,000 versus 181,000 in 2017, 195,000 in 2016, 226,000 in 2015 and 250,000 in 2014.
Monthly NFP prints are volatile. Since the 1990s, NFP prints near 300,000 have been followed by ones near or under 100,000. That has been a pattern during every bull market; NFP was negative in 1993, 1995, 1996 and 1997. The low point of 73,000 in March and 14,000 in September fit the historical pattern. This is normal, not unusual or unexpected.
Why is there so much volatility? Leave aside the data collection, seasonal adjustment, and weather issues; appreciate that a "beat" or a "miss" of 80,000 workers in a monthly NFP report is equal to just 0.05% of the US workforce.
For this reason, it's better to look at the trend; in January, trend employment growth was 1.4% yoy. Until spring 2016, annual growth had been over 2%, the highest since the 1990s. Ahead of a recession, employment growth normally falls (arrows). The continued deceleration in employment growth in the coming months continues to be an important watch out.
Employment has been driven by full-time jobs, which rose to a new all-time high in January (blue line), not part-time jobs (red line).
The labor force participation rate (the percentage of the population over 16 that is either working or looking for work) has recently stabilized, rising to a 4-year high in September. The participation rate has been falling since 2001 as baby boomers retire, exactly as participation started to rise in the mid-1960s as this group entered the workforce. Another driver is women, whose participation rate increased from about 30% in the 1950s to a peak of 60% in 1999.
Average hourly earnings growth was 2.9% yoy in January, the highest in 8 years. This is a positive trend, showing demand for more workers. Sustained acceleration in wages would be a big positive for consumption and investment that would further fuel employment.
Similarly, 4Q17 employment cost index shows total compensation growth was 2.8% yoy, the highest in the past 9 years.
For those who doubt the accuracy of the BLS employment data, federal tax receipts have also been rising to new highs (red line), a sign of better employment and wages (from Yardeni).
Demand
Regardless of which data is used, real demand has been growing at about 2-3%, equal to about 4-5% nominal.
Real (inflation-adjusted) GDP growth through 4Q17 was 2.5% yoy. 2.5-5% was common during prior expansionary periods prior to 2006.
Stripping out the changes in GDP due to inventory produces "real final sales". This is a better measure of consumption growth than total GDP. In 4Q17, this grew 2.8% yoy. A sustained break above 3% would be noteworthy.
The "real personal consumption expenditures" component of GDP (defined), which accounts for about 70% of GDP, grew at 2.8% yoy in 4Q17. This is approaching the 3-5% that was common in prior expansionary periods after 1980.
On a monthly basis, the growth in real personal consumption expenditures was 2.8% yoy in December.
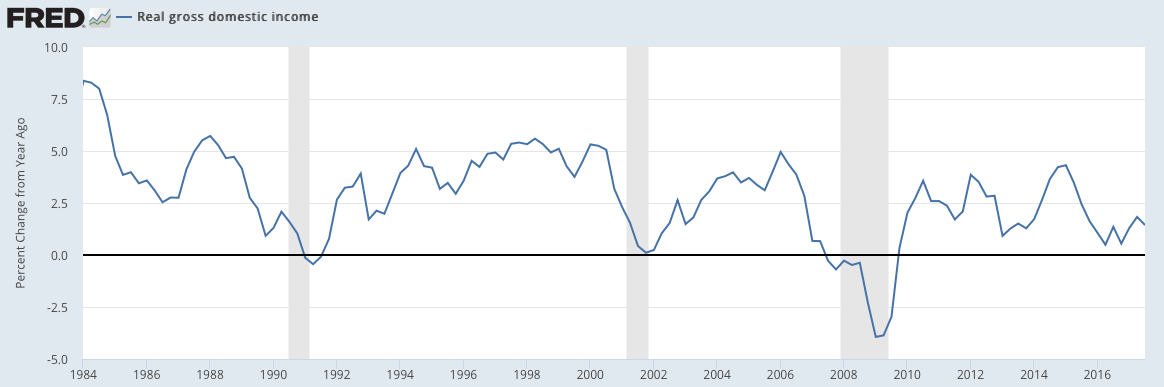
GDP measures the total expenditures in the economy. An alternative measure is GDI (gross domestic income), which measures the total income in the economy. Since every expenditure produces income, these are equivalent measurements of the economy. Some research suggests that GDI might be more accurate than GDP (here).
Real GDI growth in 3Q17 was 1.3% yoy.
Real retail sales reached a new all-time high in December, with annual growth of 3.3% yoy. The growth rate in November was the fastest in 3 years.
Retail sales in the past two years have been strongly affected by the large fall and rebound in the price of gasoline. In December, real retail sales at gasoline stations grew by 6.8% yoy after having fallen more than 20% yoy during 2016. Real retail sales excluding gas stations grew 3.0% in December. This had been on a weakening trend but now seems to be strengthening again.
Households' savings rate has fallen in the past two years. If prior expansionary cycles are a guide, GDP and consumption will continue to expand at least another 18 months even after the savings rate has bottomed and started to rise.
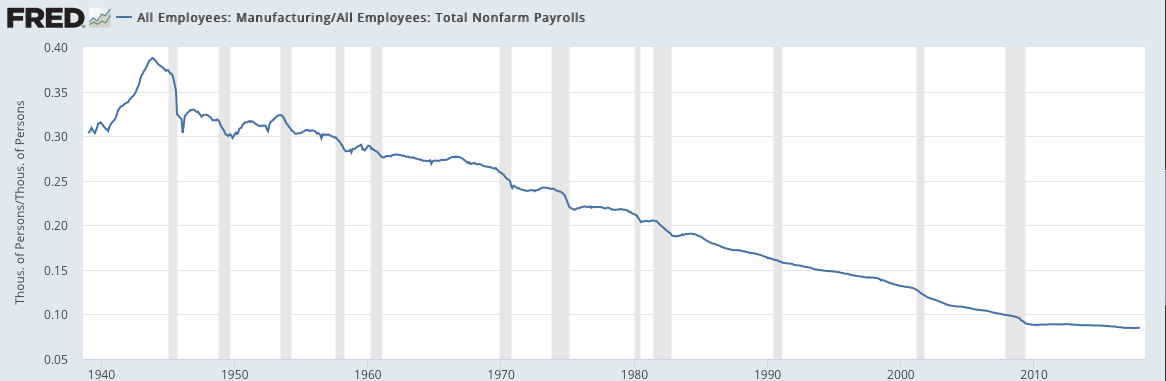
The next several slides look at manufacturing. It's important to note that manufacturing accounts for less than 10% of US employment, so these measures are of lesser importance.
Core durable goods orders (excluding military, so that it measures consumption, and transportation, which is highly volatile) rose 8.8% yoy (nominal) in December, the second-best annual growth rate in 4 years (since December 2013). Weakness in durable goods has not been a useful predictor of broader economic weakness in the past (arrows).
Industrial production (real manufacturing, mining and utility output) growth was 3.6% yoy in December. The more important manufacturing component (excluding mining and oil/gas extraction; red line) rose 2.6% yoy. This is near the best growth rate for both in over 3 years. Industrial production is a volatile series: manufacturing growth was lower at points in 2014 than it was in 2016 before rebounding strongly.
Weakness in total industrial production had been concentrated in the mining sector; the past two years had the worst annual fall in more than 40 years. It is not unusual for this part of industrial production to plummet outside of recessions. With the recovery in oil/gas extraction, mining rose 12% yoy in December.
Housing
New housing sales grew 27% yoy in November to the highest level in 10 years. Housing starts and permits are near a 10 year high although multi-family unit remains relatively weak. Overall levels of construction and sales are small relative to prior bull markets, but the trend is higher.
First, new single-family houses sold was 625,000 in December; sales in November were the highest of the past 10 years. Growth in December was 14% over the past year after growing 2% yoy in December 2016.
Second, housing starts fell 6% yoy in December after rising 11% yoy in December 2016. Starts in November were at the second highest level of the past 10 years.
Building permits are flat over the past two years (red line). Permits rose 3% yoy in December after rising 4% yoy in December 2016.
The weakness in starts (and permits) is in the multi-unit category. Single-family housing starts (blue line) reached a new post-recession high in November. Meanwhile. multi-unit housing starts (red line) has been flat over the past four years; this has been a drag on overall starts.
Inflation
Despite steady employment, demand and housing growth, core inflation remains stuck near (but under) the Fed's target of 2%.
CPI (blue line) was 2.1% last month. The more important core CPI (excluding volatile food and energy; red line) grew 1.8%.
The Fed prefers to use personal consumption expenditures (PCE) to measure inflation; total and core PCE were 1.7% and 1.5% yoy, respectively, last month. February was the first (and only) month since 2Q 2012 that total PCE was above 2%.
Some mistrust CPI and PCE. MIT publishes an independent price index (called the billion prices index; yellow line). It has tracked both CPI (blue line) and PCE closely.
Summary
In summary, the major macro data so far suggest positive but modest growth. This is consistent with corporate sales growth. SPX sales growth in both 2017 and 2018 is expected to only be about 6% (nominal).
With valuations now well above average, the current pace of growth is likely to be the limiting factor for equity appreciation. This is important, as the consensus expects earnings to grow about 12-16% in 2018 (chart from Yardeni).